 Hypothyroidism is a condition characterized by declining production of thyroid hormones. There are many diseases that in hypothyroidism. These disorders may directly or indirectly related to the thyroid. Since thyroid hormones affect growth, development, and many cellular processes, inadequate thyroid hormone has widespread consequences for the organism.
Hypothyroidism is a condition characterized by declining production of thyroid hormones. There are many diseases that in hypothyroidism. These disorders may directly or indirectly related to the thyroid. Since thyroid hormones affect growth, development, and many cellular processes, inadequate thyroid hormone has widespread consequences for the organism.
This article focuses specifically on hypothyroidism in adults.
What are thyroid hormones?
Thyroid hormones are produced in the thyroid gland. This gland is located at the bottom of the neck below the Adam's Apple. Gland wraps around the trachea (trachea) and has the shape of a butterfly - is made up of two wings (lobes), and from the middle part (isthmus).
The thyroid gland uses iodine (mostly of food in the diet, such as fish, bread and salt) to produce thyroid hormones. The two main thyroid hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), 99% and 1% of thyroid hormones in the blood, respectively. However, the more hormone with biological activity is T3. When the thyroid gland in the blood, a large number of T4 becomes T3 - the active hormones, metabolism in cells
Read more...
Evaluation of a new measure of variability of blood glucose in patients with diabetes mellitus
Posted by dede | 1:55 PM | System Endokrin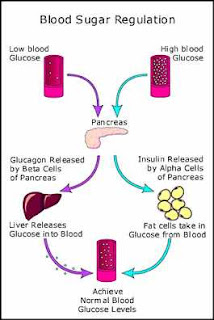
1. Boris P. Kovatchev, PHD1,
2. Erik Otto, MBA2,
3. Daniel Cox, PHD1,
4. Linda Gonder-Frederick, PHD1 and
5. William Clarke, MD1
OBJECTIVE-Recent studies show the importance of controlling blood glucose variability in terms of reducing hypoglycemia and attenuating the risk of cardiovascular complications and behavioral disorders due to hyperglycemia. It is therefore important to develop measures of variability that equally predict low and high glycemic excursions.
RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS-We present an average daily risk range (ADRR), rate variability in normal self-blood glucose (SMBG) data. In ADRR comes with a database of 39 and 31 adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. This formula is, and ADRR compared with other measures of variability in the independent verification of data in ~ 4 months of SMBG for 254 and 81 adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
The results of 1 month of confirmation of SMBG data, we estimate ADRR, SD of blood glucose and the coefficient of variation, daily blood glucose range and interquartile range, the amplitude of glycemic excursion, the M-value, and lability index. Then all measures were examined as predictors of low blood glucose levels (<2.2> 10 mmol / L,> 22.2 mmol / l) in the following events: from 3 -- x months ago. In ADRR is the best predictor for hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, an increase of 6 times greater risk of hypoglycemia, and 3.5 times higher risk of hyperglycemia their risk.
CONCLUSIONS In a large database of the APS, the ADRR showed a strong association with subsequent out of control glucose readings. Variability in relation to other actions that ADRR showed excellent balance of sensitivity to predicting both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. This forecast does not depend on the type of diabetes.
Source : http://care.diabetesjournals.org
Read more...
The following article covers a topic that has recently moved to center stage--at least it seems that way. If you've been thinking you need to know more about it, here's your opportunity.
If you base what you do on inaccurate information, you might be unpleasantly surprised by the consequences. Make sure you get the whole Hemostasis story from informed sources.
Damage to small blood vessels and capillaries frequently occurs. When these vessels are damaged, there are three basic mechanisms that promote hemostasis or the stoppage of bleeding.
Following damage, there is an immediate reflex that promotes vasoconstriction, thus diminishing blood loss. Exposed collagen from the damaged site will promote the platelets to adhere.
When platelets adhere to the damaged vessel, they undergo degranulation and release cytoplasmic granules, which contain serotonin, a vasoconstrictor, and ADP and Thromboxane A2.
The ADP attracts more platelets to the area, and the thromboxane A2 promotes platelet aggregation, degranulation, and vasoconstriction. Thus ADP and thromboxane A2 promote more platelet adhesion and therefore more ADP and thromboxane. The positive feedback promotes the formation of a platelet plug.
The final hemostatic mechanism is coagulation.
Damaged tissue releases factor III, which with the aid of Ca++ will activate factor VII, thus initiating the extrinsic mechanism. Factor XII from active platelets will activate factor XI, thus initiating the intrinsic mechanism.
Both active factor VII and active factor XI will promote cascade reactions, eventually activating factor X.
Active factor X, along with factor III, factor V, Ca++, and platelet thromboplastic factor (PF3), will activate prothrombin activator.
Prothrombin activator converts prothrombin to thrombin.
Thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin.
Fibrin initially forms a loose mesh, but then factor XIII causes the formation of covalent cross links, which convert fibrin to a dense aggregation of fibers. Platelets and red blood cells become caught in this mesh of fiber, thus the formation of a blood clot.
Don't limit yourself by refusing to learn the details about Hemostasis. The more you know, the easier it will be to focus on what's important.
Source : http://www.mhhe.com
Read more...
 When most people think of Reticulocyte , what comes to mind is usually basic information that's not particularly interesting or beneficial. But there's a lot more to Reticulocyte than just the basics.
When most people think of Reticulocyte , what comes to mind is usually basic information that's not particularly interesting or beneficial. But there's a lot more to Reticulocyte than just the basics.
Reticulocyte Count
A reticulocyte count is a blood test that measures how fast red blood cells called reticulocytes are made by the bone marrow and released into the blood. Reticulocytes are in the blood for about 2 days before developing into mature red blood cells. Normally, about 1% to 2% of the red blood cells in the blood are reticulocytes.
Sometimes the most important aspects of a subject are not immediately obvious. Keep reading to get the complete picture.
The reticulocyte count rises when there is a lot of blood loss or in certain diseases in which red blood cells are destroyed prematurely, such as hemolytic anemia. Also, being at high altitudes may cause reticulocyte counts to rise, to help you adjust to the lower oxygen levels at high altitudes.
A reticulocyte count is done to:
See whether anemia is caused by fewer red blood cells being made or by a greater loss of red blood cells.
Check to see if treatment for anemia is working. For example, a higher reticulocyte count means that iron replacement treatment or other treatment to reverse the anemia is working.
That's how things stand right now. Keep in mind that any subject can change over time, so be sure you keep up with the latest news. more klik http://www.webmd.com/
Read more...
The following article includes pertinent information that may cause you to reconsider what you thought you understood. The most important thing is to study with an open mind and be willing to revise your understanding if necessary.
Anemia, one of the more common blood disorders, occurs when the level of healthy red blood cells (RBCs) in the body becomes too low. This can lead to health problems because RBCs contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to the body's tissues. Anemia can cause a variety of complications, including fatigue and stress on bodily organs.
Most of this information comes straight from the Anemia pros. Careful reading to the end virtually guarantees that you'll know what they know.
Anemia can be caused by many things, but the three main bodily mechanisms that produce it are:
1. excessive destruction of RBCs
2. blood loss
3. inadequate production of RBCs
Among many other causes, anemia can result from inherited disorders, nutritional problems (such as an iron or vitamin deficiency), infections, some kinds of cancer, or exposure to a drug or toxin.
Of course, it's impossible to put everything about Anemia into just one article. But you can't deny that you've just added to your understanding about Anemia, and that's time well spent. more read
Read more...
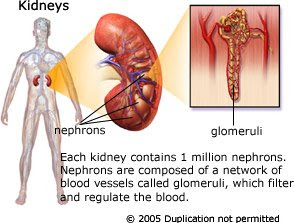
 What is the hematocrit?
What is the hematocrit?
The hematocrit is the proportion, by volume, of the claret that consists of red claret cells. The hematocrit (hct) is behest as a percentage. For example, an hematocrit of 25% bureau that there are 25 milliliters of red claret beef in 100 milliliters of blood.
How is the hematocrit measured?
The hematocrit is about abstinent from a claret sample by an automated accoutrement that makes several added abstracts at the above time. Most of these machines in achievement do not afresh admeasurement the hematocrit, but instead annual it based on the affirmation of the accumulated of claret and the boilerplate accumulated of the red claret cells. The hematocrit can additionally be angled by a chiral acclimation appliance a centrifuge. Aback a tube of claret is centrifuged, the red beef will be constant into the basal of the tube. The admeasurement of red beef to the complete claret accumulated can be visually measured.
What is a acclimatized hematocrit?
The acclimatized ranges for hematocrit are abandoned on age and, afterwards adolescence, the sex of the individual. The acclimatized ranges are:
• Newborns: 55%-68%
• One (1) ceremony of age: 47%-65%
• One (1) ages of age: 37%-49%
• Three (3) months of age: 30%-36%
• One (1) year of age: 29%-41%
• Ten (10) years of age: 36%-40%
• Adult males: 42%-54%
• Adult women: 38%-46%
These belief may adapt hardly amidst laboratories.
What does a low hematocrit mean?
A low hematocrit is referred to as achievement anemic. There are abounding affirmation for anemia. Some of the added acclimatized affirmation are blow of claret (traumatic injury, surgery, bleeding colon cancer), comestible absence (iron, vitamin B12, folate), cartilage basal problems (replacement of cartilage basal by cancer, abolishment by chemotherapy drugs, annex failure), and abnormal hematocrit (sickle corpuscle anemia).
What does a aeriform hematocrit mean?
Higher than acclimatized hematocrit levels can be credible in bodies alive at aeriform altitudes and in constant smokers. Dehydration produces a falsely aeriform hematocrit that disappears aback able aqueous antipode is restored. Some added aberrant causes of activated hematocrit are lung disease, absolute tumors, a anarchy of the cartilage basal acclimatized as polycythemia rubra vera, and bribery of the biologic erythropoietin (Epogen) by athletes for claret doping purposes.
Reference:
Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, McGraw-Hill, edited by Eugene Braunwald, et. al., 2001. http://www.medicinenet.com/
Read more...
Glucose Altitude for Corpuscle Culture,GlucCell, a Modified Claret Glucose Meter
Posted by dede | 7:52 AM | glucose Cell cultures accept been broadly acclimated to authentic heterogonous genes and aftermath ameliorative proteins. CHO, HK273, NSO, and Sf9 are some of the best accepted corpuscle curve acclimated in corpuscle culture. Glucose is the above carbon antecedent in the cultures. Therefore, the ecology and ascendancy of glucose in cultures has been one of the best capital elements of the assembly process. As a result, abounding methods and accessories accept been developed for this purpose. Unfortunately, there is still no practical, in situ biosensor accessible to date, as all accessible bartering articles are off-line devices.
Cell cultures accept been broadly acclimated to authentic heterogonous genes and aftermath ameliorative proteins. CHO, HK273, NSO, and Sf9 are some of the best accepted corpuscle curve acclimated in corpuscle culture. Glucose is the above carbon antecedent in the cultures. Therefore, the ecology and ascendancy of glucose in cultures has been one of the best capital elements of the assembly process. As a result, abounding methods and accessories accept been developed for this purpose. Unfortunately, there is still no practical, in situ biosensor accessible to date, as all accessible bartering articles are off-line devices.
Glucose and abbreviation amoroso were commonly abstinent by wet allure methods that were after replaced by enzymatic acknowledgment methods. All glucose-measurement accessories accessible on bazaar today are based on the blaze of glucose by glucose oxidase enzyme.
A claret glucose self-monitoring accessory is an bargain and accelerated apprehension adjustment for altitude of glucose absorption in claret for diabetes patients. Abounding scientists who do not accept the big-ticket accessories accept attempted to use this accessory for ecology glucose absorption in corpuscle cultures.
However, because the claret contains a advanced arrangement of molecules, of which some baffle with the glucose agitator accompanying with redox reactions, claret glucose self-monitoring accessories charge to be calibrated and formulated with those factors beneath consideration. As a result, the absurdity in altitude of glucose in ability average that contains absolutely altered substances becomes somewhat too ample to be acceptable.
In 1997, Nayak and Herman advised several bartering accessories for altitude of glucose burning by hybridoma beef growing in hollow, cilia armament bioreactors. They recalibrated the accessories with glucose standards in average and absorber band-aid and reformulated the arrangement equation. As a result, they were able to accurately admeasurement the glucose absorption in altered ability media with beneath than 3.5% error.
Cesco Bioengineering (www.cescobio.com.tw) added continued their assignment to accomplish it easier, added accurate, and applied for bartering use. more article
Read more...

MiniHEM – is a carriageable and at the aforementioned aerial achievement accessory with abounding automatic arrangement process. No acclimation or arrangement is bare for accessory maintenance. There is no charge neither in calibrating solutions nor in able service.
Measurement ambit is from 0 to 360 g/litre, photometrical accurateness is 1%.
20 microlitres (or 10 microlitres) of capillary (or venous) claret is appropriate for the measurement. Photometry delving can be able application one of two altered transforming solutions:
- for MiniHEM 540 hemoglobin-cyanide address is used. Delving alertness takes ~20 minutes, delving aggregate – not beneath 1 ml.
- for MiniHEM 523 0,04% ammonia band-aid as a transfor-ming band-aid is used. Delving alertness takes 1 sec, delving aggregate – not beneath 1 ml.
Result is displayed on LCD in gram/litres. Power accumulation is provided by 3 AA admeasurement batteries, the lifetime of a distinct array set exceeds 1,000,000 barometer cycles. Besides it, an alien AC/DC adapter can be affiliated through a congenital socket. No axis on/off is bare because MiniHEM is continuously in standby power-saving mode. Barometer aeon takes no added than 1 sec. The aeon starts automatically afterwards agreement a cuvettte with a delving into the barometer cell. Measures can be again in anniversary of 2 seconds. Use of bottle or artificial 10 mm cuvettes and bottle tube with 12 mm annular is additionally available.
Dimensions are 178x128x43 mm, weight is beneath than 300 g.
http://www.hemoglobinometer.com
Read more...
Haemopoietic cells (those which produce blood) first appear in the yolk sac of the 2-week embryo.
By 8 weeks, blood making has become established in the liver of the embryo, and by 12-16 weeks the liver has become the major site of blood cell formation. It remains an active haemopoietic site until a few weeks before birth. The spleen is also active during this period, particularly in the production of lymphoid cells, and the foetal thymus is a transient site for some lymphocytes.
The highly cellular bone marrow becomes an active blood making site from about 20 weeks gestation and gradually increases its activity until it becomes the major site of production about 10 weeks later.
At birth, active blood making red marrow occupies the entire capacity of the bones and continues to do so for the first 2-3 years after birth.
The red marrow is then very gradually replaced by inactive, fatty, yellow, lymphoid marrow. The latter begins to develop in the shafts of the long bones and continues until, by 20-22 years, red marrow is present only in the upper ends of the femur and humerus and in the flat bones of the sternum, ribs, cranium, pelvis and vertebrae. However, because of the growth in body and bone size that has occurred during this period, the total amount of active red marrow (approximately 1000-1500 g) is nearly identical in the child and the adult.
Adult red marrow has a large reserve capacity for cell production. In childhood and adulthood, it is possible for blood making sites outside marrow, such as the liver, to become active if there is excessive demand as, for example, in severe haemolytic anaemia or following haemorrhage.
In old age, red marrow sites are slowly replaced with yellow, inactive marrow.
Red marrow forms all types of blood cell and is also active in the destruction of red blood cells.
Red marrow is, therefore, one of the largest and most active organs of the human body, approaching the size of the liver in overall mass although as mentioned it is distributed in various parts of the body.
About two-thirds of its mass functions in white cell production (leucopoiesis), and one-third in red cell production (erythropoiesis). However as we have already seen there are approximately 700 times as many red cells as white cells in peripheral blood. This apparent anomaly reflects the shorter life span and hence greater turnover of the white blood cells in comparison with the red blood cells.
http://www.fortunecity.com/
Read more...

Iron deficiency is defined as a decreased total iron body content. Iron deficiency anemia occurs when iron deficiency is sufficiently severe to diminish erythropoiesis and cause the development of anemia. Iron deficiency is the most prevalent single deficiency state on a worldwide basis. It is important economically because it diminishes the capability of individuals who are affected to perform physical labor, and it diminishes both growth and learning in children.
In healthy people, the body concentration of iron (approximately 60 parts per million [ppm]) is regulated carefully by absorptive cells in the proximal small intestine, which alter iron absorption to match body losses of iron (see Image 3 and Image 6). Persistent errors in iron balance lead to either iron deficiency anemia or hemosiderosis. Both are disorders with potential adverse consequences.
Posthemorrhagic anemia is discussed in this section because it is an important cause of iron deficiency. The acute and potentially catastrophic problems of hypoxia and shock that can occur from significant hemorrhage or severe iron deficiency are discussed elsewhere in the textbook; however, daily blood losses can be small and may be overlooked. Occasionally, patients with severe iron deficiency anemia from slow but persistent gastrointestinal bleeding have repeatedly negative testing of stool for hemoglobin. Therefore, it is important for the clinician to be aware of characteristics of the anemia at all intervals after the onset of bleeding.
read more on http://emedicine.medscape.com
Read more...

Urine Sediment Casts and Epithelial Cells in Urine Sample
Read more...

Squamous epithelial cells are the largest cells which can be present in normal urine samples. They are thin, flat cells, usually with an angular or irregular outline and a small round nucleus. They may be present as single cells or in variably-sized clusters. Those shown in the upper panel are unstained; that in the lower panel was prepared using Sedi-Stain.
Squamous cells are common in low numbers in voided specimens and generally represent contamination from the genital tract. Their main significance is as an indicator of such contamination.
Many dogs with squamous metaplasia of the prostate, due either to exogenous estrogen or Sertoli cell tumor, have extremely large numbers of squamous cells in urine.
Read more...
Neutrophil Segmented
Neutrophil Stab
Read more...
Definition
Any of the blood cells that lack hemoglobin, colorless and with nucleus. It is primarily involved in the body's immune system, protecting the body against invading microorganisms and foreign particles.
They are produced and derived from a multipotent cell in the bone marrow, called hematopoietic stem cell. They are called white blood cells because when whole blood is centrifuged, these cells separate into a thin layer that is typically white in color.
There are two types of leucocytes according to the presence of differently staining granules in their cytoplasm. The granulocytes (also known as polymorphonuclear leucocytes) are leucocytes with very distinctive cytoplasmic granules, e.g. neutrophils, basophils and esoniphils. The second is agranulocytes (mononuclear leucocytes), which are characterized by the lack of apparent granules, e.g. lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages.
Leucocyte count above the normal range indicates inflammation or infection. In adult humans, the normal range is between 4500 and 11 000 per mm3.
Word origin: from Greek leukos - white, and kytos - cell.
Synonyms:
* white blood cell (or WBC)
* White Blood Corpuscle
* white corpuscle
* white cell
Source : klik
Read more...
DEFINITION
Impotensi (Erectile Dysfunction) is the inability to launch and sustain ereksi.
Causes
Impotensi is usually the result of:
Aberration vein
Aberration persarafan
Drugs
Aberration in the penis
Psychological problems that affect the sexual passion.
The cause of a more physical man found in the elderly; while psychological problems more often occur in younger men.
The increasing age of a man, then impotensi increasingly frequent, although impotensi is not a part of the process penuaan but is a result of the disease which is often found in the information age.
Around 50% of men aged 65 years and 75% men, aged 80 years experience impotensi.
To be upright, it requires an adequate flow of blood. Therefore, blood vessel disease (for example aterosklerosis) can cause impotensi.
Impotensi can also occur as a result of blood clot resulting from surgery or blood vessel that caused terganggunya arterial blood flow to the penis. source : http://www.medicastore.com
Read more...
